Real-world multimodal data
Purpose-built for early-stage cancers and earlier treatment settings
Discover novel biomarkers
Identify molecular subtypes in cancer histologies of interest, particularly powered for early-stage and/or immunotherapy-treated cancers
Characterize genetic alterations
Analyze the prevalence and prognostic or predictive impact of potential drug targets across early- and late-stage cancers
Inform clinical development
Define optimal study populations, support trial design, and assess execution feasibility
Comprehensive multimodal view of tumor biology
Broad representation across tumor types & stages
Top tumor types represented:

Colorectal

Breast
Lung

Bladder

Gastroesophageal

Melanoma
50+
tumor histologies1
70%+
patients with early-stage cancers1
~40%
US oncologists ordering from Natera1
4+
average molecular tests per patient1
Contemporary RWD for early stage cancers
Early stage cancer care is changing rapidly, driven by approval of new drugs and molecular diagnostic testing
- Assess clinical unmet need
- Identify indication expansion opportunities
- Predict control arm outcomes
- Refine patient selection approach & trial design
- Evaluate trial execution feasibility
Leverage unique longitudinal insights into molecular disease
Incorporation of molecular disease data into your RWD analysis is critical for:
- Identifying unique subpopulations of patients who are most likely to benefit from a new therapy
- Augmenting clinical data for a more comprehensive view of treatment response
What is molecular disease?
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is shed from cancer cells into the bloodstream. These tumor DNA fragments can be identified by the Signatera™ assay, offering an early, quantitative, non-invasive approach to assess treatment response and disease progression.
Across multiple studies, detection of molecular disease by Signatera™ was one of the most significant prognostic risk factors for recurrence2-6
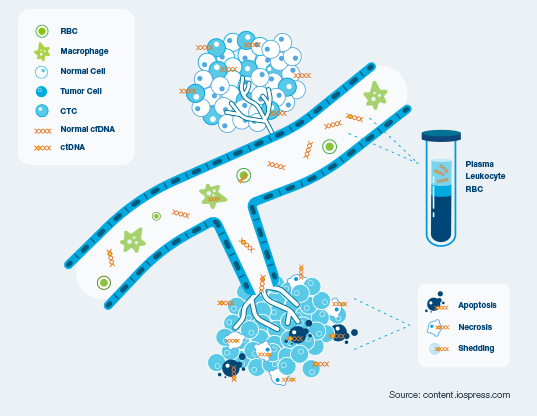
Figure 1: schematic of tumor cells and ctDNA10
Unlock new drug development opportunities with molecular disease RWD
With Natera’s technology, this unique population of molecular progressors can be identified as early as weeks after definitive treatment and months ahead of radiographic progression.2-10
Leverage Natera’s RWD to identify these opportunities and prioritize indications
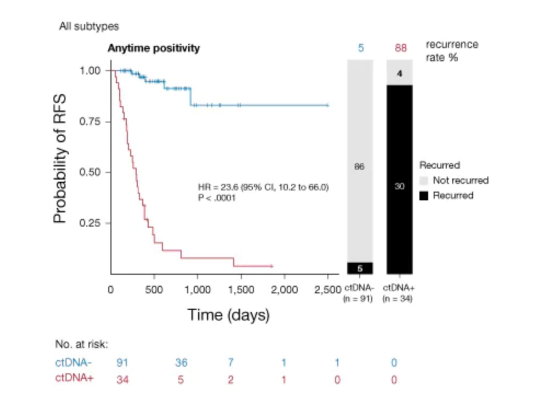
Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier estimates of real-world patients with esophagogastric cancers representing RFS as stratified by anytime ctDNA-positivity6
More comprehensive view of treatment response
Combining molecular response with clinical response can significantly improve data quality and completeness, filling critical data gaps.
Benefits of integrating molecular response data in RWD analyses:
- Quantitative: Utilize a standardized, objective response measure for readily scalable RWD analysis and mitigate confounding factors such as pseudoprogression
- Longitudinal: Frequent assessments of molecular response can provide more dynamic, real-time insights into treatment response and disease progression
- Corroborative: Increase confidence in your results by augmenting clinical data with molecular response indicators
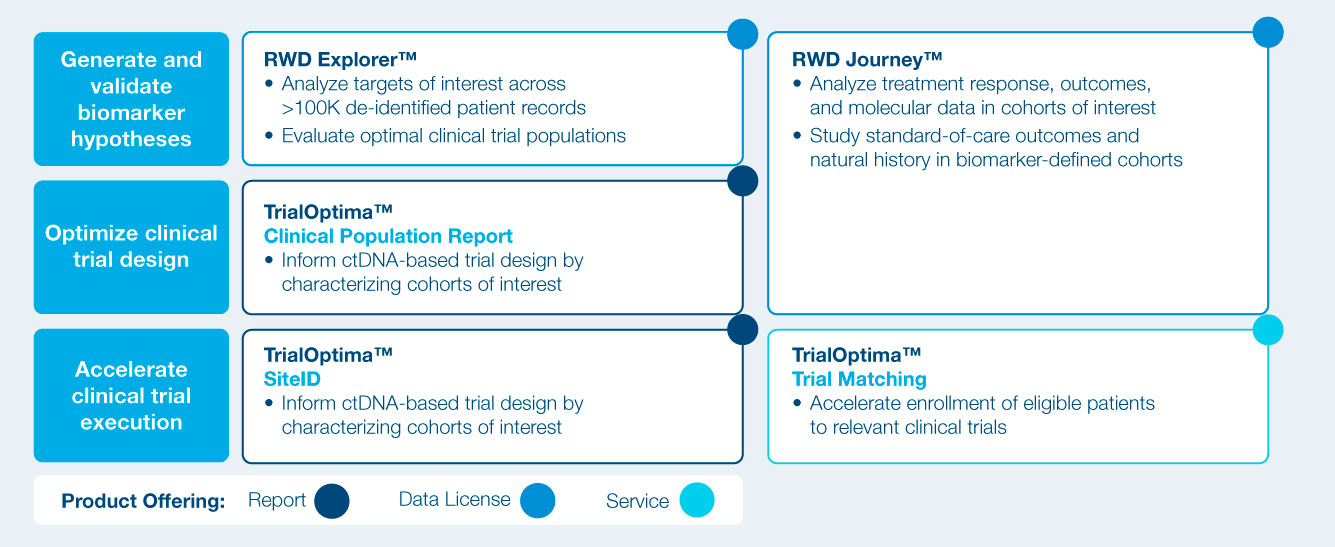
Comprehensive suite of product and services
Featured publications & presentations
Publications
- Huffman BM, Aushev VN, Budde GL, et al. Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to predict risk of recurrence in patients with esophageal and gastric cancers. JCO-Precision Oncology. 2022; 6:e2200420.
- Eroglu Z, Krinshpun S, Kalashnikova E, et al. Circulating tumor DNA based molecular residual disease detection for treatment monitoring in advanced melanoma patients. Cancer. 2023;129(11):1723-1734.
Posters & presentations
- Cohen S, Kasi P, Aushev VN, et al. Real-world monitoring of circulating tumor DNA reliably predicts cancer recurrence in patients with resected stages I-III colorectal cancer. ESMO, Paris, France, Sept 9-13, 2022. Mini Oral presentation (319MO)
- Cohen SA, Kasi PM, Aushev VN, et al. Kinetics of postoperative circulating cfDNA and impact on MRD detection rates in patients with resected stage I-III CRC. Oral presentation presented at ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium, San Francisco, CA. Jan 19-21, 2023.
- Lander EM, Rivero-Hinojosa S, Aushev VN, et al. Tumor mutational signatures in early-onset versus average-onset colorectal cancer. Oral presentation presented at ESMO GI, Barcelona, Spain, June 28 – July 1, 2023.
How can Signatera™ support your clinical trials?
Contact us to learn more
References
1Natera Q1 2024 earnings call and internal data from real-world database calculations as of July 2024.
2Kotani D, et al. Molecular residual disease and efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer. Nature Medicine. 2023.
3Yukami H, Nakamura Y, Mishima S, et al. Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) dynamics in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients with molecular residual disease: Updated analysis from GALAXY study in the CIRCULATE-JAPAN. Oral presentation presented at ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium, San Francisco, CA. Jan 18-20, 2024.
4Bratman SV, et al. Personalized circulating tumor DNA analysis as a predictive biomarker in solid tumor patients treated with pembrolizumab. Nature Cancer. 2020.
5Magbanua MJM, Swigart LB, Ahmed Z, et al. Clinical significance and biology of circulating tumor DNA in high-risk early-stage HER2-negative breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Cell. 2023;41(6):1091-1102.
6Huffman BM, Aushev VN, Budde GL, et al. Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to predict risk of recurrence in patients with esophageal and gastric cancers. JCO-Precision Oncology. 2022; 6:e2200420.
7Powles T, Assaf ZA, Davarpanah N, et al. ctDNA guiding adjuvant immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma. Nature. 2021.
8Coombes C, Page K, Salari R, et al. Personalized Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA Antedates Breast Cancer Metastatic Recurrence. Clinical Cancer Research. 2019.
9Magbanua MJM, Swigart LB, Wu H-T, et al. Circulating tumor DNA in neoadjuvant treated breast cancer reflects response and survival. Annals of Oncology. 2021.
10Abbosh C, Birkbak N, Wilson GA, et al. Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts early-stage lung cancer evolution. Nature. 2017.
